Vision to connect
Our claim is the connection of your business goals with our innovative solutions in the area of network planning, documentation and optimization.
Project
Software Defined Networking (SDN)
The task of network nodes like routers and switches is to route packages according to a routing table.
These tables are created using routing algorithms or in some cases by manual configuration.
The tables usually don't change as long as the topology of the network remains unchanged.
Thus routers and switches perform two functions: keeping their routing tables up to date according to the used routing protocols and manual configuration, and routing incoming packages according to those tables manipulated when necessary.
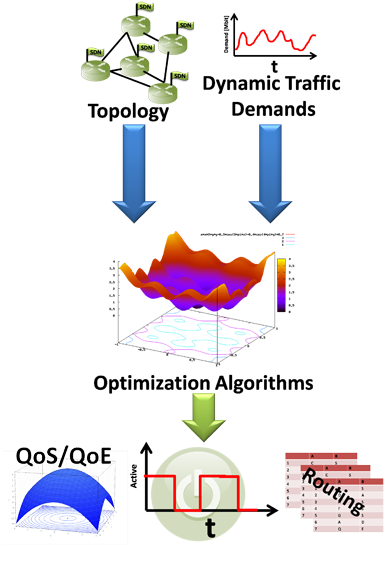
When SDN is used these functions are separated.
The nodes of a network are only routing and manipulating packages while a central controller is managing the corresponding routing tables with the advantage of a global overview of the network.
Routing tables can be adjusted in short periods of time. Depending on the load nodes and transmission lines can be shut down or turned on respectively.
In case of low load nodes and transmission lines can be shut down or turned on again in case the load is high again.
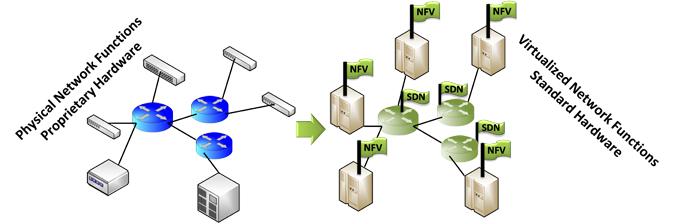
Network Functions Virtualization (NFV)
A network function is a functional block with a specified external interface and a specific functional behavior.
These include for example particular elements with specific functions in a network like HLR, SGSN, (e)NodeB, MME; signaling functions like SBC and IMS; monitoring functions, like DPI, QoE-measurements; security functions like firewall, virus scanner, intrusion detection; network-wide functions like policy control, charging platform and more.
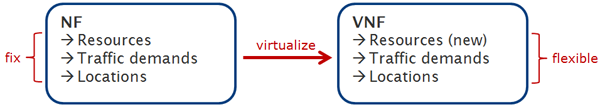
In terms of network resources functions are generally described by localization, resource demands and traffic demands.
In general those parameters are fixed but if a network function is virtualized they become adjustable.
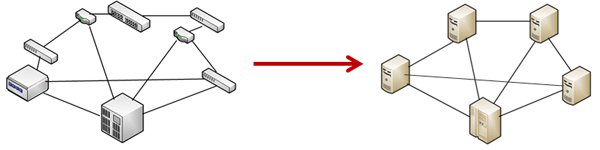
A network completely managed by NFV/SDN does not require special elements on the physical layer.
The architecture of those networks can be unified and thus can consist only of standard servers and hosts.
The architecture of those networks can be unified and thus can consist only of standard servers and hosts.
Use-Cases
Brownfield and Greenfield Scenario
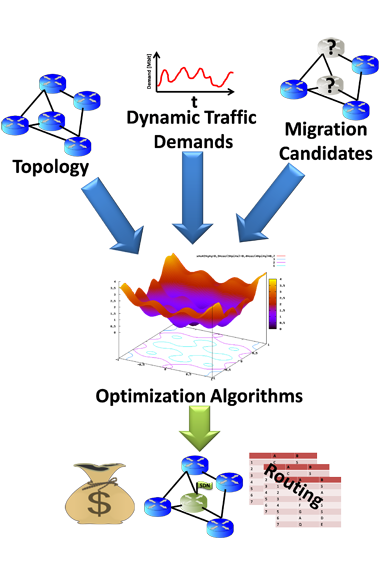
Given is a network that consists of classic switches and lines of certain capacity which are connecting them.
The routing tables are configured for managing busy hour traffic.
The excess capacity remains unused during periods of lower load usage.
Replacing all existing switches with SDN switches would allow adequate traffic control and give the possibility to shut down unused network nodes.
Generally a full replacement of all switches is very expensive and inconvenient and in particular unnecessary in most cases.
In the given scenario it is to be determined which switches should be replaced (by SDN switches) to get the most efficient network with minimal effort.
Ideal placement of Network Functions